The company’s assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and equity. Income and expenses relate to the entity’s financial performance. Individual transactions which result in income and expenses being recorded will ultimately result in a profit or loss for the period. The term capital includes the capital introduced by the business owner plus or minus any profits or losses made by the business. Profits retained in the business will increase capital and losses will decrease capital. The accounting equation will always balance because the dual aspect of accounting for income and expenses will result in equal increases or decreases to assets or liabilities.
Total debits always equal to total credits -Total Debits = Total Credits
Under which, the debit always equal to credit, and assets always equal to the sum of equities and liabilities. Accounting equation can be simply defined as a relationship between assets, liabilities and owner’s equity the accounting equation may be expressed as in the business. In double-entry accounting or bookkeeping, total debits on the left side must equal total credits on the right side. The owner’s equity is the balancing amount in the accounting equation.

The future of finance is here. Is your business prepared?
Liabilities are obligations to pay an amount owed to a lender (creditor) based on a past transaction. It is important to understand that when we talk about liabilities, we are not just talking about loans. Money collected for gift cards, subscriptions, or as advance deposits from customers could also be liabilities. Essentially, anything a company owes and has yet to pay within a period is considered a liability, such as salaries, utilities, and taxes.
Basic Accounting Equation Example – How to Calculate

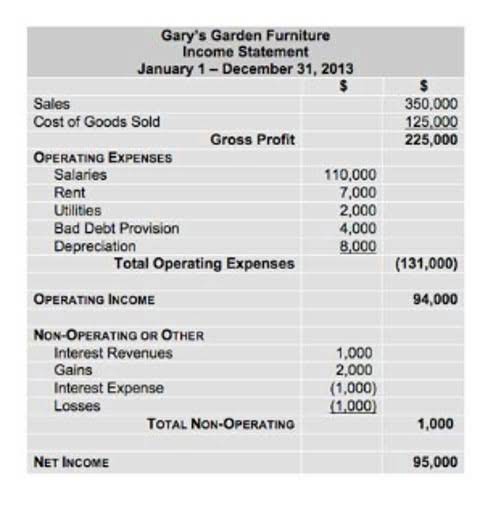
In this form, it is easier to highlight the relationship between shareholder’s equity and debt (liabilities). As you can see, shareholder’s equity is the remainder after liabilities have been subtracted from assets. This is because creditors – parties that lend money such as banks – have the first claim to a company’s assets. The balance of the total assets after considering all of the above transactions amounts to $36,450.
- Current liabilities are short-term financial obligations payable in cash within a year.
- During ABC Enterprise’s first complete month of operations, the following business transactions took place.
- Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- The owner’s equity is the value of assets that belong to the owner(s).
- A notes payable is similar to accounts payable in that the company owes money and has not yet paid.
If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset). Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. That is, each entry made on the Debit side has a corresponding entry on the Credit side.
Comprehensive Guide to Inventory Accounting
This means that the expenses exceeded the revenues for the period, thus decreasing retained earnings. The owner’s investments in the business typically come in the form of common stock and are called contributed capital. There is a hybrid owner’s investment labeled as preferred stock that is a combination of debt and equity (a concept covered in more advanced accounting courses). The company will issue shares of common stock to represent stockholder ownership. You will learn more about common stock in Corporation Accounting.

Example: How to Calculate the Accounting Equation from Transactions
- Each of these categories, in turn, includes many individual accounts, all of which a company maintains in its general ledger.
- However, when the owner’s equity is shifted on the left side, the equation takes on a different meaning.
- As a result of this transaction, the liability (accounts payable) and asset (furniture) both increased by $16,000.
- Since the company has not yet provided the product or service, it cannot recognize the customer’s payment as revenue, according to the revenue recognition principle.
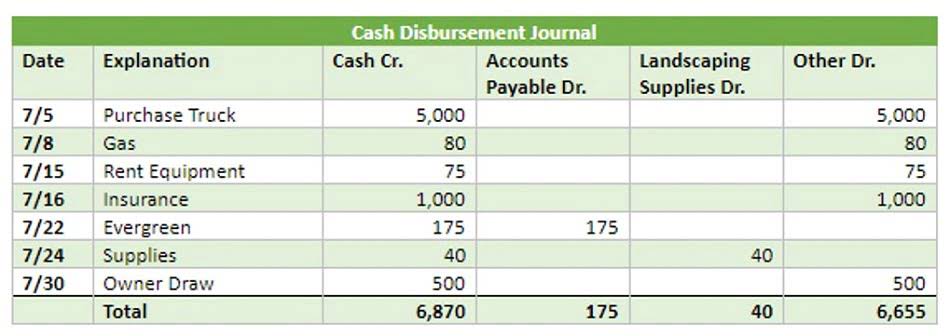
- Metro issued a check to Office Lux for $300 previously purchased supplies on account.
- Journal entries often use the language of debits (DR) and credits (CR).